Exploring What Fat Cells Are and Their Role in Our Body
As you embark on the journey to understanding your body’s complexities, you’ll find that fat cells, otherwise known as adipocytes, play an interesting and significant role. This article takes you through the nuances of these fascinating cells – exploring their very nature, their godsend ability to aid weight loss by activating the beneficial brown fat cells, to the often debated question of their permanence in your body. Additionally, it casts a light on the fat-burning hormone found primarily in muscle cells. So buckle up and prepare yourself to amplify your awareness about the pivotal role of fat cells in your body’s grand scheme.
Understanding Fat Cells
The human body is composed of numerous types of cells and each cell plays an important part in ensuring the proper functionality of the body systems. Among these different cell types, fat cells play an essential role in numerous bodily processes. In this article, we will explore fat cells at a deeper level, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of what they are, their structure, and their function in the human body.
Definition of Fat Cells
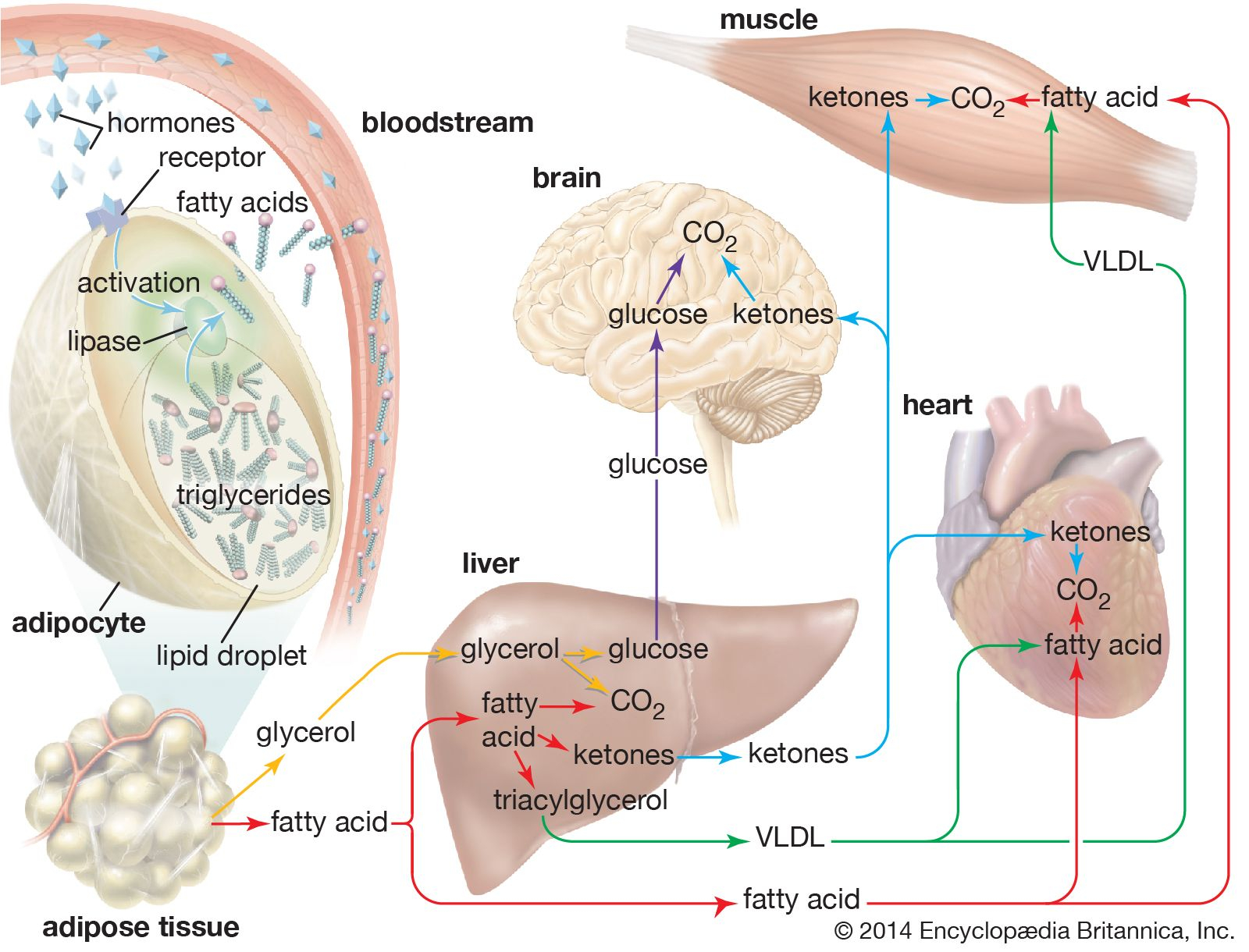
Fat cells, also known as adipocytes, are specialized cells responsible for storing excess energy from the food you eat in the form of fat. They serve as the body’s energy bank, releasing stored energy whenever your body needs it. Fat cells are not solely an energy storehouse; they play vital roles in temperature regulation, cushioning organs, and producing hormones important to metabolism and immune function.
Types of Fat Cells: White, Brown, and Beige
There are primarily two types of fat cells in the human body: white and brown fat cells. White fat cells are the most common, making up 90% of the body’s adipose tissue, and store energy as a single large fat droplet. Alternatively, brown fat cells have multiple smaller droplets and a high number of mitochondria, which give them their brown color and burn energy to generate heat. Recently, a third type of fat cell, known as beige or brite (brown-in-white), has been discovered. Beige cells function similarly to brown fat cells and can be found scattered within white fat tissue.
Structure of Fat Cells
Understanding the structure of fat cells is key to understanding how they work.
Cell Composition
A fat cell is composed of a large lipid droplet surrounded by a thin layer of cytoplasm that contains all of the cell’s organelles, including the nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum. The lipid droplet is made up of triglycerides and cholesteryl esters, the molecules responsible for energy storage.
How Fat Cells Store Energy
When you consume more calories than your body needs for immediate energy needs, the excess energy is converted into triglycerides and stored in the lipid droplet of fat cells. This fat can be broken down and used as energy when needed.
Formation and Growth of Fat Cells
Fat cells form during childhood and adolescence, and the number usually stays constant in adulthood.
Fat Cell Development
Fat cells stem from precursor cells and proceed through a process called adipogenesis to become mature adipocytes. During this phase, they attain the ability to store and release energy efficiently.
How Fat Cells Multiply and Expand
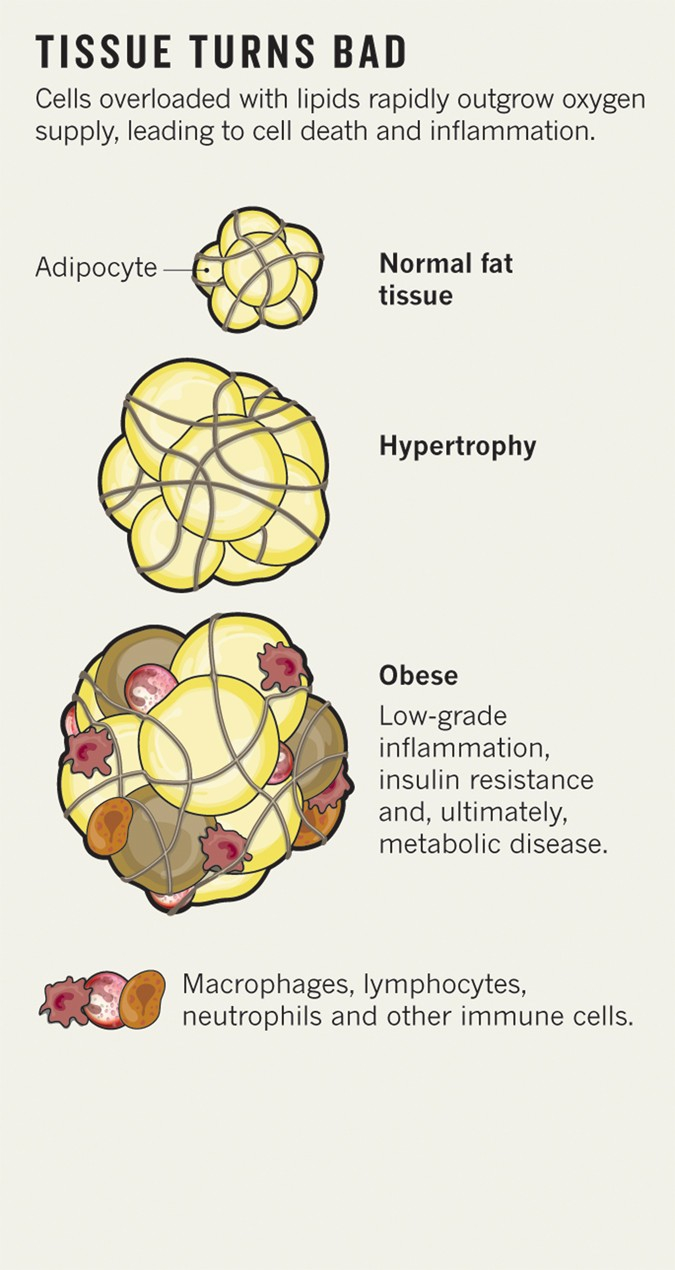
Once fat cells have developed, the number remains fairly constant throughout adult life. When more energy is consumed than is burned, existing fat cells expand to store the extra energy. If these fat cells reach their maximum size and more storage is needed, the body can produce more fat cells.
Fat Cells and Weight Gain
Weight gain and obesity are closely related to the function and behavior of fat cells.
Role of Fat Cells in Obesity
In a situation where calorie intake constantly surpasses calorie expenditure, fat cells continue to expand, leading to weight gain and possibly obesity. Obesity, in turn, can contribute to the development of numerous health problems, such as heart disease and diabetes.
How Fat Cells Contribute to Weight Gain
Fat cells contribute to weight gain by storing excess calories as fat. The body can expand existing fat cells or make new ones to accommodate the excess energy.

Destruction and Removal of Fat Cells
The removal or destruction of fat cells has become a popular topic in the context of weight loss.
Can Fat Cells be Destroyed?
To an extent, yes. While the number of fat cells typically remains constant in adults, weight loss can reduce the size of fat cells but not their number. However, certain procedures and treatments can destroy fat cells.
Methods of Fat Cell Removal: Liposuction and CoolSculpting
Liposuction is a surgical procedure that removes fat cells, leading to a reduction in body fat. On the other hand, CoolSculpting is a non-invasive procedure that targets and freezes fat cells, resulting in their natural death and removal from the body.
Function of Fat Cells in the Body
In addition to energy storage, fat cells serve a number of other essential functions in the body.
Energy Storage
As previously mentioned, fat cells play a crucial role in energy storage. When you take more energy in than your body needs, the excess is stored as fat, which can be used later when energy demands exceed intake.
Thermal Insulation
Brown fat cells, in particular, play an essential role in generating heat, thus providing thermal insulation that helps maintain body temperature.
Hormone Production
Fat cells are also endocrine organs that produce and release hormones, which regulate numerous bodily functions such as appetite, metabolism, and inflammation.

Activating Brown Fat Cells for Weight Loss
Activating brown fat cells is a potential approach to boost energy expenditure and lose weight.
Differences Between White and Brown Fat Cells
Unlike white fat cells that store energy, brown fat cells burn energy to produce heat, thus making them an attractive target for weight loss.
Methods to Activate Brown Fat Cells
Certain strategies, like regular exercise, cold exposure, and consuming food that increases metabolic rate, have been suggested to activate brown fat cells.
Fat Cells and Exercise
Exercise plays a key role in managing body fat levels.
Effect of Exercise on Fat Cell Size
Regular exercise helps reduce the size of fat cells by burning stored energy for fuel. Exercise also promotes the conversion of white fat cells into brown-like fat cells, further enhancing metabolic rate and energy expenditure.
Fat Burning Hormone Found in Muscle Cells
The hormone irisin, found in muscle cells, can stimulate the conversion of white fat cells into brown-like cells. This hormone’s release increases during exercise, providing another link between exercise and fat loss.

Fat Cells and Nutrition
The foods we consume can have a significant influence on our body’s fat cell health and growth.
Role of Diet in Fat Cell Health
A well-balanced diet can help maintain healthy fat cells by providing the necessary nutrients for their proper function while avoiding overconsumption that leads to fat cell expansion.
How Certain Nutrients Affect Fat Cells
Some nutrients, including certain types of fats and sugar, contribute to fat cell expansion, while others, like fiber, protein, and healthy fats, can help manage weight and promote fat loss.
Fat Cells and Diseases
Certain diseases are associated with abnormal behavior of fat cells.
Lipodystrophies and Other Fat Cell Disorders
Lipodystrophies are a group of disorders characterized by the abnormal distribution of fat cells in the body, leading to metabolic complications such as insulin resistance and diabetes.
Fat Cells and Chronic Diseases Like Diabetes and Heart Disease
Obesity and excess fat storage are linked to several chronic diseases, including diabetes and heart disease. Excess fat can cause inflammation and hormonal imbalances, which contribute to the development of these conditions. Understanding fat cells and how to manage their health is therefore a pivotal aspect of maintaining overall health.
In summary, fat cells play numerous essential roles in the human body. From energy storage and hormone production to thermal insulation, these cells are crucial to our well-being. However, it’s equally important to pay attention to fat cell health, as their mismanagement can lead to several disorders and diseases. Proper nutrition, regular exercise, and a balanced lifestyle are fundamental to ensuring the healthy function of our fat cells.


Pingback: +["obesity Is A Chronic Disease Related To Diet, Which Requires A Rigorous Medical Treatment To"]
Pingback: Unleashing The Secret: How To Get Rid Of Fat Cells For Good