Why Is Obesity At Its Worse
As we gaze at the global health landscape, it becomes quite clear that obesity is high on our list of concerns. It has reached an unprecedented level, thus posing severe threats to our health. This article sheds light on the disturbing rise of obesity, a daunting factor that could shorten our lives significantly. We take on the challenging fight against it and seek to comprehend its horrifying escalation, exploring the critical question: “Why is obesity at its worst?” Together we will journey through the complex factors that have contributed to the issue, probing into the very crux of this global health crisis.
Understanding Obesity
Definition of Obesity
Obesity is a complex health condition described by an unhealthy or excessive accumulation of body fat. It’s often defined medically using the body mass index (BMI), a measurement derived by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. People are categorized as obese when their BMI is 30 or more.
Medical Perspective on Obesity
From a medical perspective, obesity is not only about weight. It’s recognized as a chronic disease that can cause or aggravate numerous other health conditions, including diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer. It’s not just about aesthetics, but about overall health and longevity. Medical professionals emphasize that obese individuals are at a high risk for a broad array of health issues and often employ a comprehensive approach towards its treatment.
Social Perspective on Obesity
Obesity is often stigmatized in society, leading to a variety of social and psychological problems like body shaming, bullying, and discrimination. People struggling with obesity often face negative stereotypes, prejudice and are sometimes even excluded from social activities. These issues underscore the need for a wider cultural shift towards an understanding and empathetic approach to obesity.
Obesity Rates Throughout History
Obesity Rates in the Past
Historically, obesity was less prevalent. The focus was more on famine and scarcity, making excess weight a symbol of prosperity and a sign of good health. However, the situation has changed dramatically in recent decades due to advancements in food manufacturing, agriculture, and transportation, leading to an influx of high-energy, low-cost foods, and increasingly sedentary lifestyle.
Comparison of Obesity Rates Over the Decades
over the last few decades, obesity rates have risen at an alarming rate. The World Health Organization necessitated a declaration of a global epidemic as far back as 1997. This rapidly growing prevalence has been seen in both adults and children.
Current Obesity Rates
According to recent statistics, an estimated 650 million adults and 380 million children and adolescents are obese. This accounts for about 13% of adults and 7% of children and adolescents globally – nearly tripling since 1975.
Current Global Obesity Situation
Global Prevalence of Obesity
In the current global situation, no country is untouched by the obesity epidemic. The prevalence has increased in every corner of the world, with a higher frequency observed in urban areas due to lifestyle and dietary factors.
Countries With the Highest Obesity Rates
Some countries, particularly high-income western countries, report excessively high obesity rates. As per World Population Review, Nauru has the highest prevalence of obesity, followed closely by Cook Islands, Palau, and Marshall Islands. Among larger countries, the United States tops the list.
Countries With Increasing Obesity Rates
While higher-income countries have had high obesity rates for some time now, low- and middle-income countries, especially urban areas, have also witnessed a sharp rise in obesity rates. Asia, Africa, and Latin America are seeing significant increases as changes in diet and lifestyle become more widespread.
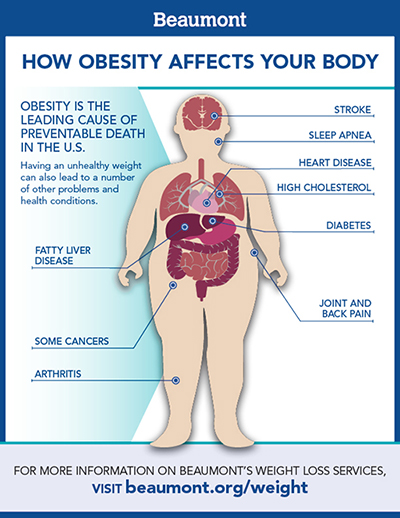
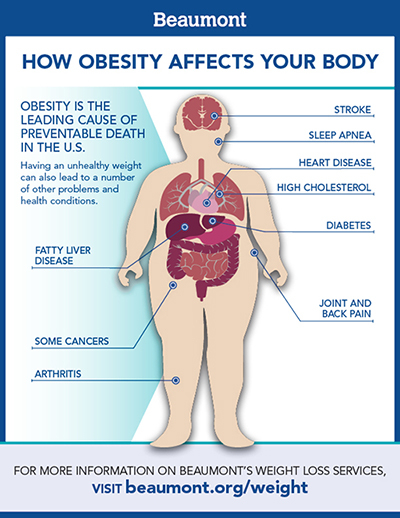
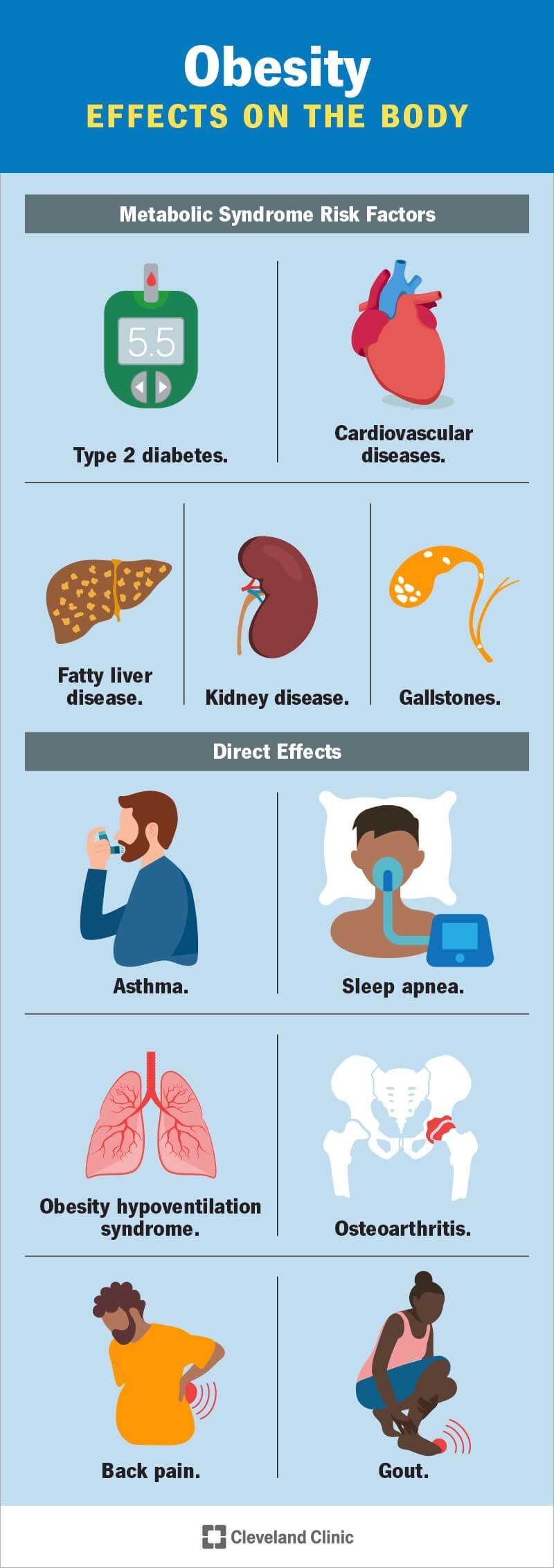
Impacts of Obesity on Health
Physical Health Complications Associated With Obesity
obesity is associated with numerous physical health complications. These include high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, gallstones, sleep apnea, osteoarthritis, fatty liver disease, kidney disease, and pregnancy problems in women.
Psychological Impacts of Obesity
Obesity can also have profound psychological impacts, such as depression, eating disorders, distorted body image, and low self-esteem. Social stigma and discrimination can further exacerbate these issues, emphasizing the need for comprehensive and empathetic care for those struggling with obesity.
Obesity and Life Expectancy
Research conclusively shows that obesity significantly reduces life expectancy. It’s associated with an increased risk of premature death due to related diseases and complications. obesity can shorten a person’s lifespan by up to 8-10 years, equivalent to the effects of lifelong smoking.

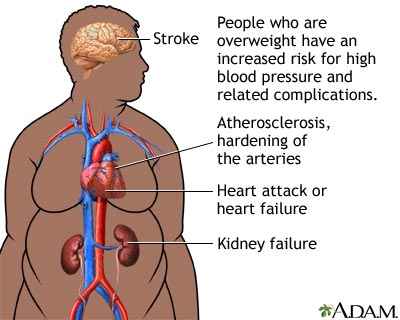
Link Between Obesity and other Diseases
Obesity and Heart Diseases
obesity is strongly linked to heart diseases since excessive body fat increases blood pressure and cholesterol levels, leading to a higher risk of coronary artery diseases. It also affects the heart’s structure and function, further increasing the risk of heart failure.
Obesity and Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is another disease closely associated with obesity. About 90% of people living with type 2 diabetes are overweight or obese. Excess fat, especially abdominal fat, leads to insulin resistance, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels.
Obesity and Cancer
Several types of cancer are linked to obesity, including breast, colon, kidney, esophagus, and pancreatic cancer. The exact mechanisms remain uncertain, but it may be due to chronic low-level inflammation or hormonal imbalance caused by excess body fat.
Role of Diet in Obesity
Impact of High Calorie Diets
A high-calorie diet, especially when combined with physical inactivity, significantly contributes to the risk of obesity. Foods high in fat and sugar but low in essential nutrients can lead to weight gain as the body stores unused calories as fat.
Importance of Nutritional Knowledge
Understanding the nutritional value of food is vital in combating obesity. Awareness of energy balance, food portions, and the nutritional content of meals can empower individuals to make healthier food choices.
Effects of Highly Processed Food
Highly processed foods, often high in fat, sugar, and salt but low in fiber and nutrients, have been linked to weight gain and obesity. These foods are typically cheap, convenient and engineered to taste good, encouraging overconsumption.
Role of Lifestyle and Physical Activity
Sedentary Lifestyle and Obesity
A sedentary lifestyle, characterized by prolonged periods of inactivity, increases the likelihood of becoming obese. This lifestyle has become common due to changes in work habits, transportation, and increased leisure time.
Impact of Physical Inactivity
Physical inactivity directly contributes to weight gain by disrupting the balance between calorie intake and calorie burning. Inactivity also increases the risk of other conditions associated with obesity, such as heart disease and diabetes.
Benefits of a Physically Active Lifestyle
Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy body weight by burning excess calories that would otherwise be stored as fat. In combination with a balanced diet, it forms the cornerstone of obesity prevention and management.
Societal Influence on Obesity
Impact of Societal Norms and Expectations
Societal norms and expectations play a powerful role in shaping dietary habits and lifestyle. Rapid urbanization, high-paced living, and the ‘culture of convenience’ can encourage unhealthy behaviors contributing to obesity.
Influence of Media and Advertising
Advertising and media heavily influence food choices, particularly through the marketing of high-calorie, low-nutrition foods and beverages. Children and adolescents are especially vulnerable to such marketing tactics.
Socioeconomic Factors Contributing to Obesity
Socioeconomic factors are major contributors to obesity. Low-income groups are often more susceptible to obesity due to limited access to healthy food options, high-stress levels, and fewer opportunities for physical activity.

Efforts to Reduce Obesity Rates
Effective Weight Loss Strategies
effective weight loss strategies include administering a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and behavioral changes. Medical interventions, such as drug therapy and surgery, are used when these primary treatments are ineffective.
Role of Government Regulations and Policies
Government regulations and policies play a crucial role in managing the obesity epidemic. This may include implementing nutrition labeling, taxing unhealthy food and beverages, and creating policies to promote physical activity.
Health Campaigns Against Obesity
National and international health campaigns aim to raise awareness about the dangers of obesity and promote healthy habits. These campaigns can effectively influence public perceptions and behaviors towards obesity.
Future Predictions and Preventive Measures for Obesity
Foreseen Trends in Obesity Rates
Unless significant preventive steps are taken, the prevalence of obesity is expected to continue rising. Projections suggest that the global obesity rate may reach 18% in men and surpass 21% in women by 2025.
Strategies to Reduce Future Obesity Rates
Preventing obesity requires well-coordinated strategies. These include promoting healthy diets and regular physical activity, improving health education, and creating supportive environments that enable healthy choices.
Importance of Preventive Measures
Preventive measures are the most effective solution to the obesity epidemic. Making lifestyle changes, such as healthy eating and regular physical activity, improving societal norms, and implementing solid public health policies, can go a long way in reversing this global health crisis.

Pingback: Why Is Obesity A Disease
Pingback: Which Of The Following Conditions Is Thought To Contribute To The Development Of Obesity?
Pingback: What Is The Weight Of Obesity For Women Ovet 50