Understanding What Causes Weight Loss in Cancer Patients
It’s not uncommon for weight loss to be one of the many concerns when dealing with cancer. Looking at the issue head on, “Understanding What Causes weight loss in cancer patients” examines the reasons behind the phenomenon, crystalizing it in plain language. Let’s cut through the medical jargon as the article addresses both rapid weight loss in general and specific causes in the context of cancer. By the end of this, you’ll have a whole new understanding of the relationship between cancer and weight loss.

Understanding Cancer-induced Weight Loss
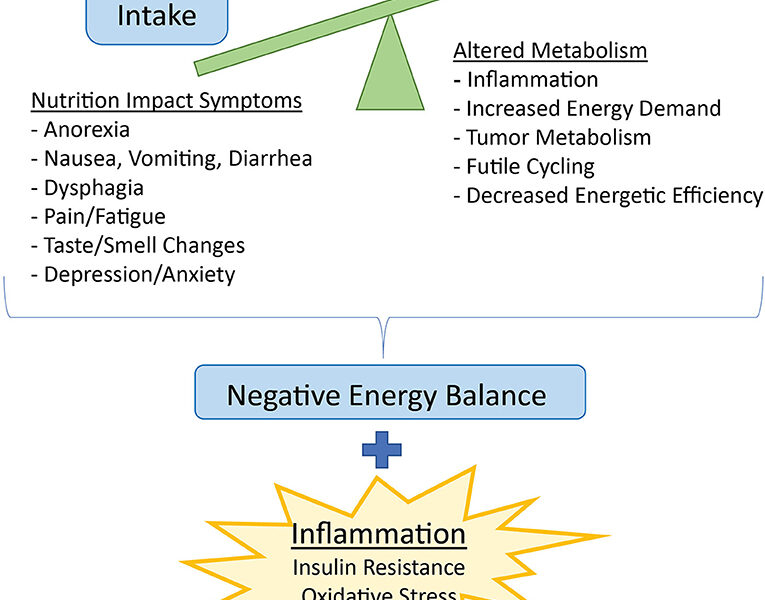
Cancer-induced weight loss, sometimes referred to as cancer cachexia, is a complex metabolic condition characterized by the progressive loss of muscle and fat tissue. The loss of weight and muscle mass, often accompanied by weakness, can significantly reduce your ability to perform daily activities or resist infections. By understanding how cancer can contribute to weight loss, you can better manage it and minimize its impact on your body.
Defining Cancer-induced Weight Loss
When your body loses weight without you trying to lose weight, it could be due to cancer. In fact, cancer-induced weight loss is often one of the first noticeable symptoms of this disease. You may not notice a change in your appetite or eating habits, but unexpectedly begin to lose pounds. This phenomenon can be mystifying and alarming, but it’s a common effect of various types of cancers.
Physical Implications of Cancer-induced Weight Loss
Cancer-induced weight loss can have a significant impact on your body. Not only does it weaken your immune system, impairing your body’s ability to fight off the disease, but it can also lead to increased vulnerability to infections. This can further complicate the course of cancer treatment. Moreover, weight loss can result in muscle weakness and fatigue, making routine activities feel strenuous.
Psychological Impact of Cancer-induced Weight Loss
Cancer-induced weight loss does not only affect you physically but can also take a toll on your emotional well-being. Seeing your body change can bring about feelings of insecurity, fear, and sadness. It can drastically affect your self-esteem and quality of life. The weight loss, along with the stress of dealing with a cancer diagnosis, can contribute to mental health issues like depression and anxiety.
Types of Cancers that Often Result in Weight Loss
It’s important to note that not all cancers result in weight loss. However, some types of cancers are more commonly associated with this phenomenon.
Pancreatic Cancer and Weight Loss
Pancreatic cancer is notorious for causing significant weight loss. This can be attributed to the fact that the pancreas plays a vital role in digestion and the absorption of nutrients. When it’s affected by cancer, your body cannot get the nutrients it needs, leading to weight loss.
Lung Cancer and Weight Loss
Lung cancer can also result in weight loss. As the cancer progresses, it can interfere with your appetite or cause difficulties in swallowing, leading to decreased food intake. Additionally, the energy expenditure during breathing might be higher in patients with lung cancer, further contributing to weight loss.
Colon Cancer and Weight Loss
Colon cancer may lead to weight loss due to changes in bowel habits. You might experience symptoms such as diarrhea or constipation, which can affect your ability to absorb nutrients.
Gastric Cancer and Weight Loss
Gastric cancer affects the stomach, which plays a significant role in digestion. As a result, you may experience loss of appetite, difficulty eating large meals, and feeling full quickly, leading to inadequate nutrient intake and subsequent weight loss.
Lymphoma and Weight Loss
With lymphoma, weight loss might occur due to the increased energy requirement of the body to fight the disease. The immune response might also affect your metabolism leading to weight loss.

Physiological Mechanisms Behind Cancer-induced Weight Loss
Cancer-induced weight loss is due to a combination of reduced food intake and changes in the way the body metabolizes nutrients.
Metabolic Changes with Cancer
Cancer can cause metabolic changes leading to wasting, a condition known as cachexia. Your metabolic rate—or the speed at which your body uses calories—might increase, causing you to burn calories faster than you’re taking them in.
Energy Imbalance in Cancer Patients
Cancer cells require a high amount of energy to grow and reproduce. This energy demand may take precedence over the normal physiological needs of your body, leading to an energy imbalance.
Role of Inflammatory Proteins
Cancer can ignite an inflammatory response in your body. Inflammatory proteins are released, which can interfere with normal digestion and absorption processes, affecting your nutrient and energy intake and utilization.
Tumour’s Impact on Nutrition Absorption
Tumors can physically obstruct your digestive tract or cause a reduction in the functional capacity of vital organs involved in digestion and absorption. This can interfere with nutrient absorption and contribute to weight loss.
Role of Appetite Loss in Cancer-induced Weight Loss
Appetite loss or anorexia is a common symptom among cancer patients and directly influences weight loss.
Understanding Appetite Loss in Cancer Patients
Appetite loss in cancer patients can occur due to a variety of factors including treatment side-effects, cancer-related fatigue, or the psychological stress associated with the diagnosis. This can result in decreased food intake leading to weight loss.
Reasons for Appetite Loss
The reasons for appetite loss in cancer patients are multifaceted, ranging from altered taste and smell perception to more severe symptoms such as nausea and vomiting induced by chemotherapy.
Effects of Appetite Loss on Weight
Without a regular intake of adequate nutrients, your body might start using its fat and muscle stores for energy, causing weight loss.

Impact of Cancer Treatments on Weight Loss
Treatment modalities like chemotherapy and radiation therapy can significantly impact weight in cancer patients.
Role of Chemotherapy in Weight Fluctuations
Chemotherapy can lead to side effects like nausea, vomiting, mouth sores, and taste changes, which can decrease your appetite and food intake. Moreover, it can cause fluid retention, leading to weight gain, and further complicating the weight management process.
Radiation Therapy and Weight Loss
Radiation therapy, particularly when applied to the gastrointestinal tract, can cause a decrease in appetite, inflammation, and changes in taste, leading to weight loss.
Role of Cancer-related Fatigue and Weight Loss
Cancer-related fatigue can interact with other symptoms to compound weight loss in cancer patients.
Defining Cancer-related Fatigue
Cancer-related fatigue is a persistent feeling of tiredness or exhaustion related to cancer or cancer treatment. It can be emotionally, mentally, and physically debilitating and is different from the fatigue experienced by healthy individuals.
How Cancer-related Fatigue Contributes to Weight Loss
The energy drain of cancer-related fatigue can make preparing and eating food feel like an overwhelming task. This can lead to a reduced food intake, tipping the scale towards an energy deficit and weight loss.
Impact of Cancer-related Fatigue on Daily Life
Cancer-related fatigue can make it difficult to perform everyday activities. The overwhelming fatigue can deplete your appetite, further impacting your daily nutritional intake and contributing to weight loss.

Cancer Cachexia and Weight Loss
Cachexia is a severe form of weight loss seen in some cancer patients.
Understanding Cancer Cachexia
Cancer cachexia involves a significant loss of body weight, including both muscle and fat, and is often accompanied by extreme weakness and fatigue. It affects the majority of patients in advanced stages of cancer and can be life-threatening.
Physiological Mechanisms of Cachexia
Cachexia arises from a combination of reduced calorie intake and a metabolic imbalance caused by the cancer’s effect on the body’s metabolism. Increased inflammatory response and altered hormone levels can also contribute to the development of cachexia.
Treatment Approaches for Cachexia
Managing cachexia involves improving dietary intake, employing certain medications, and engaging in regular physical activity. It’s important to work with your healthcare team to come up with a suitable and manageable treatment plan.
Managing Weight Loss in Cancer Patients
Comprehensive management of weight loss in cancer patients encompasses nutritional changes and, in some cases, pharmacological interventions.
Importance of Nutrition Management
Good nutrition is critical for maintaining your weight and supporting your body during cancer treatment. Dieticians play an essential role in helping create a nutritious meal plan accommodating your changing taste preferences and appetite.
Creating a Balanced Diet Plan
A balanced diet includes proteins for muscle repair, carbohydrates and fats for energy, and vitamins and minerals for optimal functioning of the immune system. Each meal should ideally have a source of protein, whole grain, and colorful fruits and/or vegetables.
Role of Supplements and Meal Replacements
In some cases, you may find eating difficult or may not feel hungry. In such situations, supplements and meal replacements can play an important role in ensuring you’re getting the necessary nutrients in your diet.
Pharmacological Interventions to Curb Weight Loss
Medications to stimulate appetite, address metabolic changes, and tackle mental health issues can help curb weight loss in cancer patients.
Use of Appetite Stimulants
Appetite stimulants can help increase your appetite, enabling you to consume more calories and sustain your weight.
Medications to Counteract Metabolic Changes
Certain medications can help counteract the metabolic changes associated with cancer, suppressing inflammation and improving protein synthesis in the muscles.
Treatment of Underlying Depression or Anxiety Causing Weight Loss
Depression and anxiety are common among cancer patients, which may further reduce their appetite and cause weight loss. Treating these underlying mental health issues could help improve your appetite, dietary consumption, and potentially prevent further weight loss.
Psychological Support and Counseling for Weight Management
Addressing the psychological aspects is equally important when dealing with cancer-induced weight loss.
Role of Therapy and Counseling
Therapy and counseling can provide emotional support to help you cope with the psychological impact of cancer-induced weight loss. Therapists can provide effective strategies to improve body image and self-esteem, and manage anxiety and depression, all of which can influence your nutritional status.
Support Groups for Weight Management
Participation in support groups can also be beneficial. Connecting with others who are going through similar challenges can create a sense of belonging and provide practical advice on managing weight loss.
Importance of Family and Social Support
Family and social support play a critical role in managing cancer-induced weight loss. A supportive network can provide emotional encouragement, help with meal preparation, and ensure you’re making healthy food choices.
In conclusion, cancer-induced weight loss is a complex and multifaceted issue. It’s important to understand the underlying mechanisms contributing to weight loss, the types of cancer commonly associated with it, and the physical and psychological implications. It is equally crucial to recognize the role treatment modalities, appetite loss, fatigue, and cachexia play in this process. By being proactive about managing your weight and using a comprehensive approach involving nutritional management, pharmacological interventions, and psychological support, you can better cope with this aspect of living with cancer.

Pingback: Understanding What Can Cause Sudden Weight Loss In Dogs