The Type Of Obesity Where Fat Is Stored Primarily In The Abdominal Area
Encircling a complex and critical health struggle, we find ourselves carried on a whirlwind journey into the heart of obesity, specifically the kind where fat primarily besieges the abdominal area. This silent enemy, lurking beneath the surface, has proven itself a significant catalyst, fast-tracking a myriad of life-threatening diseases, ultimately birthing an untimely farewell to a vibrant life. Combating this adversary becomes an imperative mission, necessitating an intricate understanding of all its nuances and chameleon-like manifestations. The focus is set not just on obesity—a haunting global health peril—but specifically on the variant where fat decides to make the belly its playground.

Understanding Obesity
Definition of Obesity
Before we commence our exploration, we must first understand what obesity represents. Obesity is more than just an increase in body weight; it’s a chronic and relapsing disease marked by an accumulation of excess body fat that may impact health. It is generally determined by the Body Mass Index (BMI), a calculation that considers both a person’s weight and height.
Global Prevalence of Obesity
Much to our concern, obesity is a global epidemic, exploding across every continent and infiltrating the lifestyle of millions. According to the World Health Organization, obesity has nearly tripled since 1975. In 2016, it was reported that more than 1.9 billion adults were overweight, and of these over 650 million were obese.
Impacts of Obesity on Health
Our health is our wealth and obesity is a well-known thief. It has serious impacts on our health, becoming the breeding ground for life-threatening diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancers. Additionally, obesity can create difficulties in mobility, psychological distress, and a decreased quality of life.
Types of Obesity
General Obesity
Obesity is not a single entity, it comes in multiple shapes and forms. General obesity, as the term suggests, is characterized by an overall excess of body fat. It covers the entire body without favoring any particular region.
Abdominal Obesity
We then encounter abdominal obesity, a specific and problematic form of obesity. Here, fat primarily accumulates in the abdominal area, leading to an expanded waistline and often referred to as the “apple” body type. This type of obesity is of particular concern due to its association with various health complications.
Gynoid Obesity
Next on our cards is gynoid obesity, where fat is predominantly distributed around the hips, buttocks, and thighs, producing a “pear” body shape. While it may pose less of a health risk than abdominal obesity, it shouldn’t be underestimated.
Metabolically Healthy Obesity
Lastly, we have metabolically healthy obesity (MHO), an anomaly that stands out in the crowd. Despite having a body mass index (BMI) in the obese category, those with MHO do not suffer from the metabolic complications typically associated with obesity.
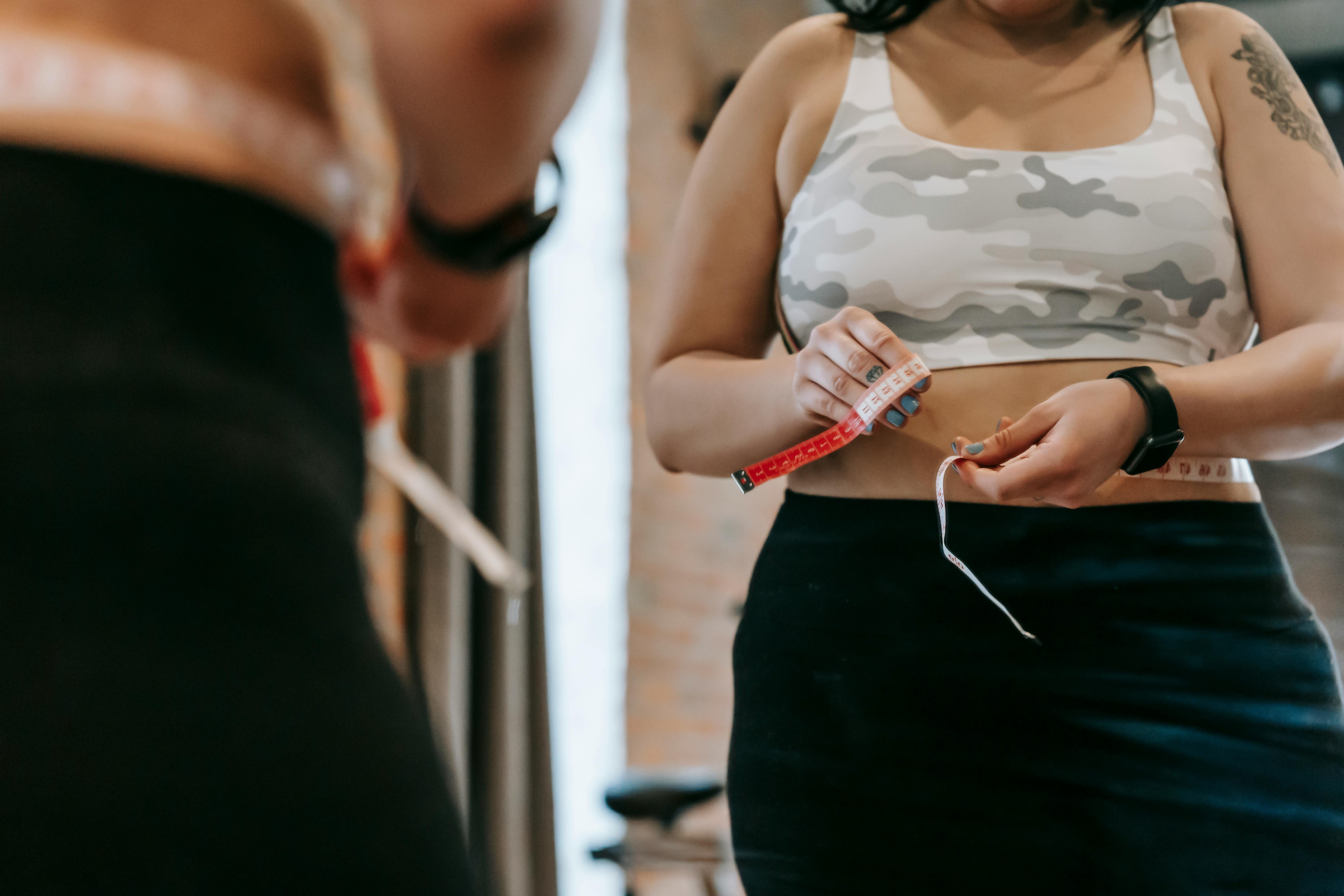

Characteristics of Abdominal Obesity
Specific Definition of Abdominal Obesity
As we delve deeper into the world of obesity, let’s understand the specifics of abdominal obesity. It is the accumulation of excess fat around the stomach area, which poses higher health risks. It transforms the shape of the body into an apple-like form, with fat concentrated in the waist area.
Differences between Abdominal Obesity and Other Types
Each type of obesity carries its own baggage, and abdominal obesity is no different. Abdominal obesity differs not only in the shape of the body but also the location of fat deposition – the belly area, which can directly affect major organs increasing the chance of developing heart diseases, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
Major Indicators of Abdominal Obesity
One of the most direct indicators of abdominal obesity is a high waist circumference or waist-hip ratio. Besides, increased belly fat, feeling tired due to carrying additional weight, and facing difficulty in mobility could be major indicators.
Causes of Abdominal Obesity
Genetic Factors
While stepping into the domain of causality, let’s remember that our genes play a vital yet unpredictable role in shaping us. Certain genetic factors may predispose us to abdominal obesity. For some, the journey towards abdominal obesity begins before birth, coded in their DNA.
Dietary Habits
The food we eat writes the story of our health. Unhealthy dietary habits – overconsumption of high-calorie, sugar-laden foods, and lack of fiber contribute to gaining excess abdominal fat.
Lack of Physical Activity
A sedentary lifestyle is a contributing factor to obesity, especially abdominal obesity. Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight balance, while inactivity may lead to weight gain.
Stress and Hormonal Imbalance
The role of stress and hormonal imbalance cannot be overlooked in causing abdominal obesity. Chronic stress and hormonal changes can promote fat storage in the abdominal region.
Health Risks Associated With Abdominal Obesity
Increased Risk of Heart Diseases
The journey of abdominal obesity is often accompanied by an increased risk of heart diseases. The deluge of fat around the waist adds undue pressure on the heart, increasing the risk of hypertension, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases.
Greater Possibility of Developing Type 2 Diabetes
Abdominal obesity also significantly increases the risk of Type 2 diabetes. Excess fat can make cells resistant to the effects of insulin, which regulates blood sugar. When this happens, blood sugar levels can rise dramatically leading to diabetes.
Links with Metabolic Disorders
The onslaught of abdominal fat doesn’t stop at diabetes and heart disease; it also acts as a catalyst for metabolic disorders. The excess belly fat impairs metabolism and leads to conditions such as metabolic syndrome.
Influence on Mental Health
The specter of abdominal obesity can shroud mental health in darkness. Obesity leads to self-esteem issues, depression, and other mental health issues, creating a vicious cycle of physical and psychological distress.
Detecting Abdominal Obesity
Common Signs of Abdominal Obesity
To detect abdominal obesity, we first look for physical signs such as an increased waist circumference. Feeling out of breath quickly or difficulty in physical mobility can also signal abdominal obesity.
Medical Examinations and Tests
Medical examinations and specific tests can formally diagnose abdominal obesity. Besides waist circumference, blood tests to measure glucose, cholesterol, and other metabolic markers can be performed.
Body Mass Index (BMI) and Waist-to-Hip Ratio
Body Mass Index (BMI) is another key tool that helps determine if a person has abdominal obesity. A high BMI is often associated with increased body and, in particular, abdominal fat. Waist-to-hip ratio, where waist circumference is divided by hip circumference, is another measure used to diagnose abdominal obesity.

Preventing Abdominal Obesity
Healthy Diet Recommendations
A healthy diet is a powerful tool in preventing abdominal obesity. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and low-fat dairy can help maintain a healthy weight and ward off the onset of obesity.
Importance of Regular Exercise
Regular exercise is another strong weapon to prevent this disease. Regular physical activity helps to maintain a healthy body weight and reduces the risk of excess fat accumulation around the abdomen.
Stress Management Techniques
Managing mental health is an important aspect of preventing obesity. Stress management techniques such as meditation, deep-breathing, and yoga can help control the body’s stress response and keep abdominal obesity at bay.
Role of Medications and Surgery
Lastly, in some cases, preventative measures also include medications and bariatric surgery. These are usually advised for those at high risk of obesity due to genetic factors or other medical conditions.
Managing Abdominal Obesity
Effective Dietary Changes
Management of abdominal obesity involves effective dietary changes such as portion control, inclusion of more fiber, and reduction of saturated fat and simple sugars in the diet. Consulting a dietician can help customize an effective diet plan.
Exercise Programs for Abdominal Obesity
Undertaking a regular exercise program specifically designed for abdominal obesity is also crucial. These programs often include a mix of cardiovascular exercises and strength training.
Medical Interventions
Medical interventions, such as medications or surgeries, may be recommended in cases where lifestyle changes alone are not enough to reduce abdominal obesity. These interventions aim to restrict absorption of fat or decrease appetite.
Psychological Support
Last but crucial, psychological support plays a valuable role in managing abdominal obesity. Counseling and support groups can provide emotional support and help individuals adhere to their lifestyle changes.
Latest Research on Abdominal Obesity
Recent Scientific Findings
Science is endlessly exploring the abyss of abdominal obesity. New findings suggest that besides lifestyle factors, inflammation and gut bacteria may play a role in abdominal fat accumulation.
Advancements in Treatment Options
Moreover, the science of healing is evolving at a rapid pace. The advent of better medication, advancements in bariatic surgeries, and development of new non-invasive procedures mark the progress in the treatment of abdominal obesity.
Research on Genetic Factors Influencing Abdominal Obesity
A flurry of research is currently underway to uncover the intricate genetic factors influencing abdominal obesity. Unraveling these genetic mysteries could lead to personalized treatments and preventive strategies.
Overcoming Obstacles in Battling Abdominal Obesity
Dealing with Societal Stigma Against Obesity
The battle against obesity is not just physical but also sociocultural. Overcoming societal stigma and misconceptions about obesity is key to enabling effective obesity management.
Changing Mindset About Body Image and Health
A change in mindset about body image and health is also needed. Not all body sizes are unhealthy and understanding this is important in the fight against obesity-related stigma.
Access to Affordable Healthy Food and Exercise Options
Economic barriers often hinder access to healthy food and exercise options. Efforts should be made to improve accessibility and affordability of these essentials for everyone, irrespective of their social or economic status.
Support from Healthcare Professionals
Initiating change needs reinforcements and healthcare professionals play a crucial role here. Providing support, guidance, and effective treatment plans is fundamental to help individuals confront and manage obesity.
In conclusion, obesity, more specifically abdominal obesity, is a significant health concern worldwide. However, through understanding, lifestyle changes, preventative measures, faith in scientific progress and communal support, we can challenge, manage and slowly, but surely overcome abdominal obesity.

Pingback: Unveiling the Appearance of 30 Pounds of Fat - Lose Weight With Absolute Minimal Diet - Your All In One Guide to Weight Loss & Nutrition
Pingback: Misconceptions about Body Fat: Lessons from Sophie - Lose Weight With Absolute Minimal Diet - Your All In One Guide to Weight Loss & Nutrition