Examining Fat Soluble Vitamins in Relation to Sophie’s Body Fat
“Examining Fat Soluble Vitamins in Relation to Sophie’s Body Fat” brings light to the intricate correlation between fat-soluble vitamins and its implications on an individual’s body fat percentage. It takes the case of Sophie, who has a total body fat percentage of 30%, falling within the healthy body fat range. As the narrative navigates through the seemingly complex labyrinth of fat-related concerns, it dispels many myths surrounding body fat, one being which is not a fat soluble vitamin, as well as debunking ill-informed ideas about what a pound of fat genuinely looks like. It also addresses the lesser-discussed topics concerning fat and its diverse impact on the body, ranging from the crucial role healthy fats play in our diet, to the significance of essential body fat, and even down to the aesthetic aspects such as the visual comparison of differing fat quantities.
Understanding Fat Soluble Vitamins
Definition of Fat Soluble Vitamins
Fat-soluble vitamins are a group of vitamins that require fat for absorption and storage in the body. They are stored mainly in the liver and adipose tissues, also known as fat cells, and can stay in the body for a longer stretch of time, reducing the need for frequent intake.
Types of Fat Soluble Vitamins
There are four types of fat-soluble vitamins – A, D, E, and K, each of which has a set of crucial tasks in maintaining good health. Unlike water-soluble vitamins that are expelled by the body regularly, fat-soluble vitamins are kept in reserve for when they are needed.
Functions of Fat Soluble Vitamins
These vitamins have a significant role in a range of bodily functions. Vitamin A, for instance, is critical to vision, immune system function, and reproduction. Vitamin D is pivotal to calcium metabolism, bone health, and certain immune functions. Vitamin E acts as an antioxidant, preserving cells from damage and aiding in immune function. Lastly, vitamin K is essential for coagulation, making sure blood clots properly to prevent excessive bleeding.
Sophie’s Body Fat Percentage
Interpretation of Sophie’s Body Fat Percentage
Sophie’s total body fat is 30%, which places her in a healthy body fat range for women, as per the American Council on Exercise guidelines. A body fat percentage of 25-31% is considered healthy for women, implying that Sophie falls within the healthier range.
Comparison with Average Body Fat Percentages
Compared to the average body fat percentage, Sophie’s body fat is somewhat above-average for women. The average body fat percentage for women is 25-28%, so while Sophie’s body fat is still within the acceptable breadth, it could be potentially lower.
Measurement Techniques for Body Fat Percentage
Techniques for measuring body fat percentage include bioelectrical impedance analysis, dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry, skinfold measurement, hydrostatic weighing, and air displacement plethysmography. The chosen method frequently depends on available resources, accessibility, and individual preference.
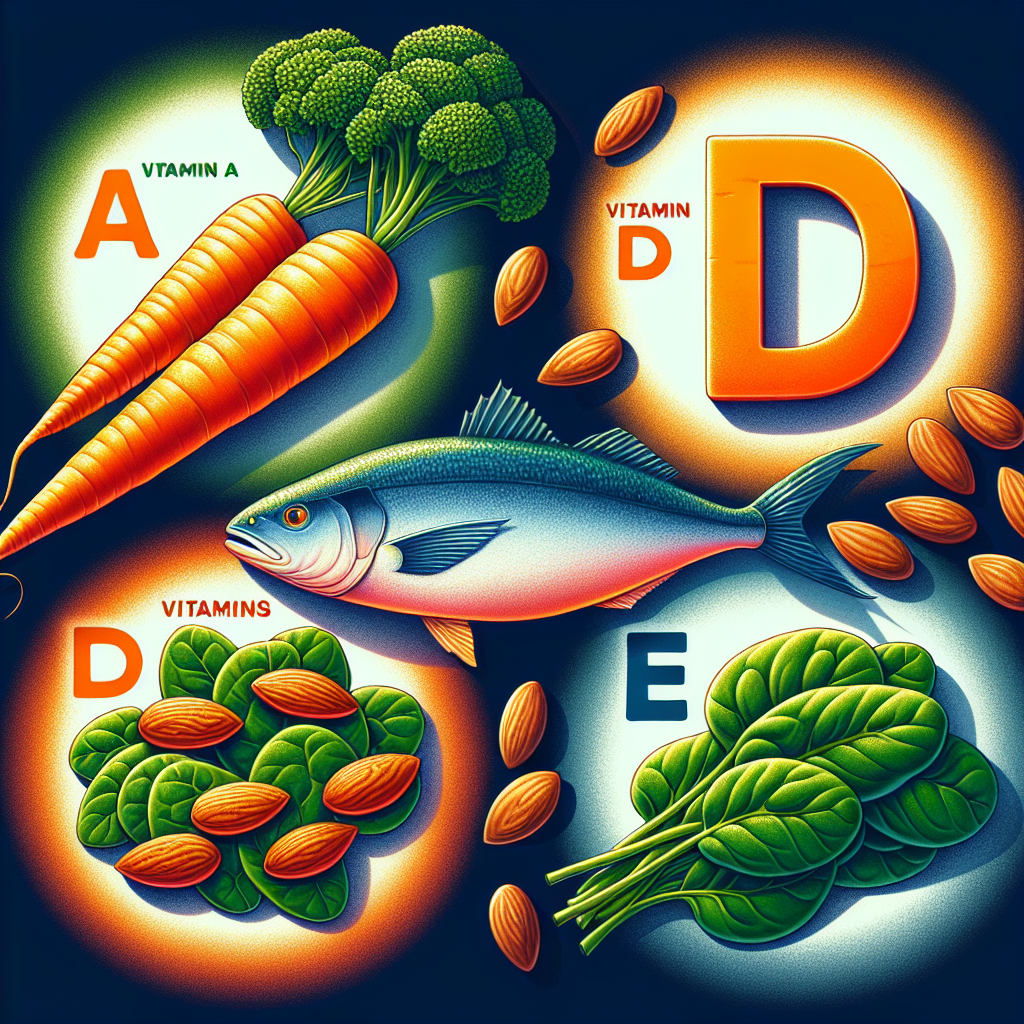

The Role of Fat Soluble Vitamins in Body Fat
Influence on Metabolism
Fat-soluble vitamins can have a profound impact on metabolism. Vitamins A, D, E, and K aid in nutrient metabolism, such as the metabolism of fats and proteins. For instance, vitamin A helps regulate the genes responsible for breaking down fats.
Contribution to Fat Storage
Fat-soluble vitamins, as their name suggests, are stored in the body’s fat tissues. Storing these vitamins ensures their availability for usage whenever the body requires them, nonetheless, it can contribute to an increased body fat percentage.
Assisting in Breakdown of Body Fat
Certain fat-soluble vitamins can assist in the breakdown of body fat. For example, vitamin D has shown potential in facilitating fat breakdown and reducing the development of new fat cells.
Fat Soluble Vitamin Deficiencies and Excess
Consequences of Vitamin A, D, E, K Deficiencies
Deficiencies in fat-soluble vitamins can lead to a spectrum of health issues. Vitamin A deficiency can weaken the immune system and impair vision, while insufficient vitamin D can contribute to osteomalacia and rickets in children. Vitamin E deficiency can lead to neurological issues due to damage of the nervous system, and inadequate vitamin K can result in excessive bleeding.
Impact of Fat Soluble Vitamin Overconsumption on Body Fat
Overconsumption of these vitamins tends to lead to an accumulation in body fat, which could potentially increase body fat percentage. Although rare, it can also lead to toxicity since these vitamins are stored within the body and not easily expelled.
Importance of Balance in Vitamin Intake
Balance in vitamin intake is crucial as both deficiency and excess can entail health problems. Considering that fat-soluble vitamins are stored in the body, daily intake is not always necessary, and a well-adjusted diet should provide adequate amounts of these vitamins.
Impact of Fat Soluble Vitamins on Physical Fitness
Vitamins’ Role in Energy Production
Fat-soluble vitamins, particularly Vitamins A and K, play an essential role in energy production. For instance, Vitamin K is required for the synthesis of certain proteins needed for energy metabolism.
Effects on Muscle Growth and Recovery
Fat-soluble vitamins are critical for muscle growth and recovery. Vitamins A and D are vital for muscle growth, strengthening, and the prevention of muscle weakness or muscle wasting diseases.
Influence on Exercise Performance
Insufficient intake of these vitamins can negatively impact exercise performance. Vitamins A and D, in particular, play an essential role in maintaining performance by supporting bone health and strengthening muscle function.
Managing Body Fat through Diet
Incorporating Fat Soluble Vitamins into Diet
Integrating fat-soluble vitamins into the diet is key for overall health. Foods rich in these vitamins include dairy products, fish oil, fruits, and green leafy vegetables.
Controlling Caloric Intake and Output
Managing caloric intake and output is crucial in controlling body fat. Despite the benefits of fat-soluble vitamins, they should be consumed responsibly to avoid caloric excess and subsequent fat storage.
Understanding Macronutrient Balances
Comprehension of macronutrient balances is another essential aspect of managing body fat. While it’s necessary to ensure adequate intake of fat for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, a careful balance must be maintained.
Sophie’s Diet and Lifestyle Choices
Evaluation of Sophie’s Dietary Habits
Considering Sophie’s body fat percentage, a comprehensive assessment of her dietary habits would provide valuable insight. It would be beneficial to ensure that she consumes the right balance of macronutrients, including adequate amounts of fat for fat-soluble vitamin absorption.
Impact of Exercise on Sophie’s Body Fat
Regular exercise, apart from helping in controlling Sophie’s body fat percentage, can also support the uptake of fat-soluble vitamins. It boosts metabolism, helping in the quicker uptake and utilization of the vitamins.
Analyzing Sophie’s Lifestyle for Optimum Vitamin Absorption
Optimizing lifestyle habits can ensure maximum absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and beneficial impacts on body fat levels. Elements to analyze include meal timing, patterns of physical activity, and the quality of foods consumed.
Recommendations for Maintaining Healthy Body Fat
Establishment of Healthy Routines
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, that includes regular physical activity and balanced diets, can aid in managing body fat percentages effectively.
Suggestions for Adequate Fat Soluble Vitamin Intake
Fat-soluble vitamin consumption should be adequate, involving vitamin-rich foods like fish, fruits, green leafy vegetables and dairy. It is also important to incorporate sufficient amounts of healthy fats into the diet to facilitate the absorption of these vitamins.
Benefits of Variety in Diet and Exercise
Variety in diet and exercise can lead to overall wellness and efficient management of body fat. Regular changes in exercise routines can enhance fitness levels, while diversity in diet ensures the intake of a wide range of nutrients.
Body Fat Myths and Misconceptions
Addressing Common Body Fat Stereotypes
Common stereotypes such as ‘fat is bad’ need to be addressed. While keeping body fat under control is valuable, it is also necessary for absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, energy storage, and as protection against physical injuries.
Difference between Essential Body Fat and Storage Body Fat
Understanding the difference between essential body fat (required for the body to function) and storage body fat (excess calories stored in the form of adipose tissue) is important for a comprehensive view on body fat.
Misunderstanding about Low Body Fat Dangers
Low body fat is often misinterpreted as healthier, however, extremely low body fat can lead to a lack of essential body fat, impairing the function of the body, including the balance and metabolism of fat-soluble vitamins.
Case Studies: Fitness Journey Transition from Fat to Fit
Documenting Personal Experiences
Personal experiences documented by individuals who have successfully gone through a “fat to fit” transition offer valuable insight. These journeys highlight the importance of dietary changes, regular exercise, and disciplined lifestyle alterations.
Impact of Fat Soluble Vitamins on Transformation
These success stories also underscore the role of fat-soluble vitamins in these transformations. Adequate intake of these vitamins often plays a vital role in maintaining energy levels, improving metabolic rates, enhancing muscle growth and recovery.
Body Fat Management Strategies Discussed
These case studies often elaborate on body fat management strategies that have worked well. This mainly includes balanced diets and well-planned exercise routines. Controlling the intake of high calorie and processed foods, regular physical activity, balanced nutrient intake, and an overall active lifestyle are common elements in most successful stories.

